A very common doubt among users is to prove that the document has been signed electronically. The only thing necessary for this is to open the pdf itself, as it contains all the signature data and evidence that serves to prove its authenticity.
Once we know how to digitally sign a PDF, Viafirma’s system collects the different types of signatures and evidences that are incorporated to the document itself that we will be able to see in Adobe.
All the information necessary to prove that the document has been electronically signed can be seen in the signature panel and in the XML files attached to the pdf once the signing process has been completed.
Let’s take a look at some examples to see where all these data are to be found.
Sign with digital certificate
We are used to electronically signed documents being identified with a signature stamp as follows:

It is a visual element that has information about the firm, as well as the website and QR code where we can check the details of the firm, but it is not really essential.
What is really important, as we have said, is the data contained in the file.
Once the pdf has been electronically signed with a digital certificate, if we open it in Adobe we will see something like this:
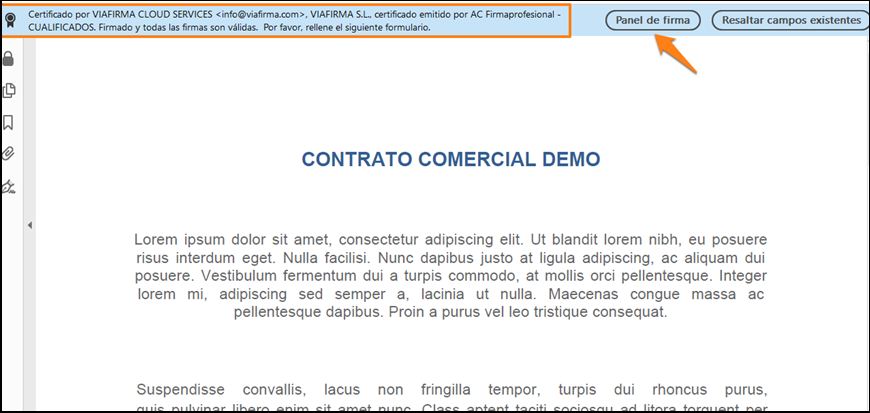
The system instantly recognises that the document has been electronically signed with a valid certificate.
It is easily recognisable as an informative message appears at the top of the screen indicating “Certified by VIAFIRMA CLOUD SERVICES, VIAFIRMA,S.L. certificate issued by AC Firmaprofesional” together with access to the signature panel. If we click on it, we will see the details of the certificate to check the electronic signature.
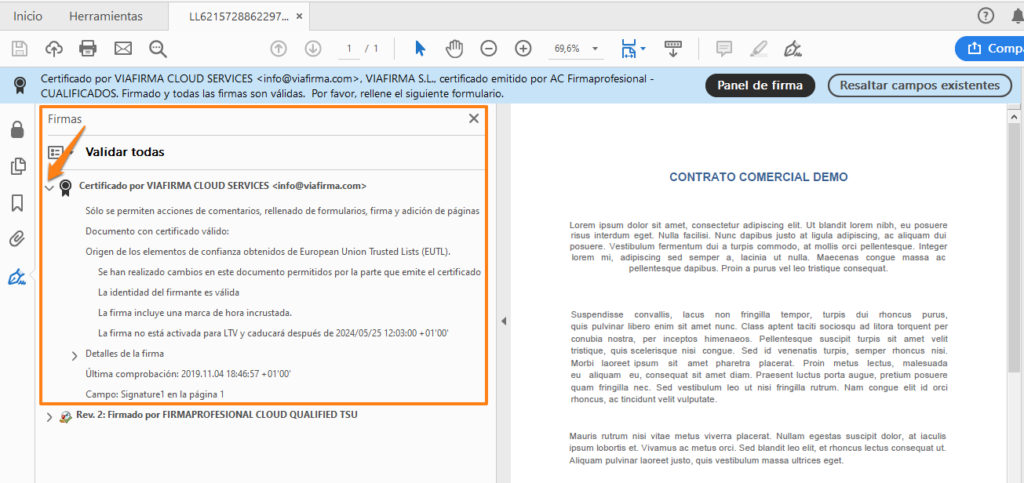
Further details of the certificate can be found in the properties:
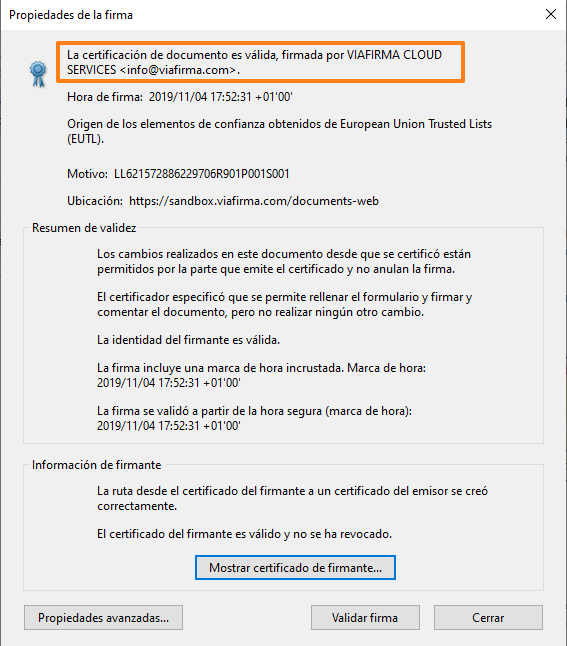
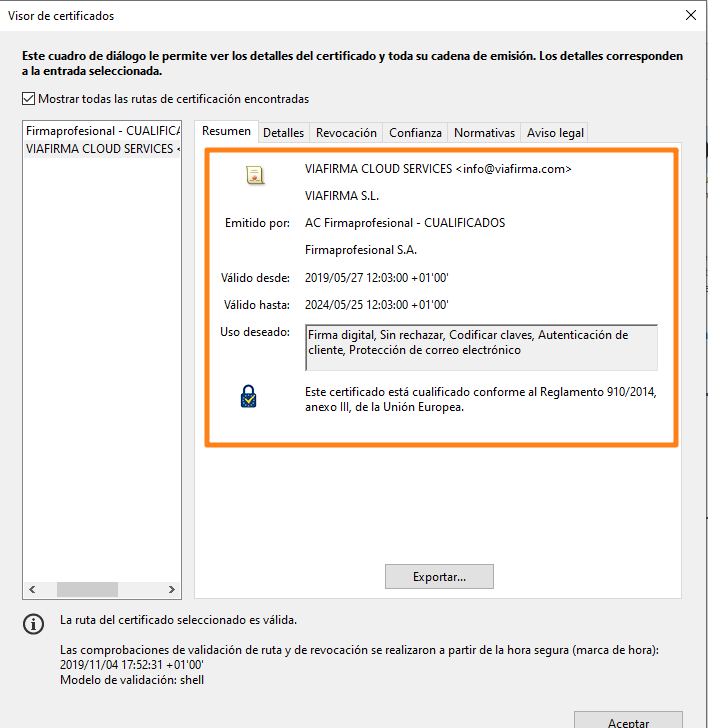
By signing the document with a digital certificate, the document cannot be altered at a later date, thus guaranteeing its integrity (if it is modified, Adobe itself will alert you to this fact when you open it).
Electronically signed document with SMS OTP

The OTP-SMS (temporary code sent by SMS to the signatory’s mobile phone) is represented by the round seal we see. It is really just an image, which can in fact be customised with any other image. The information that really matters is the one that appears in the document attachment.
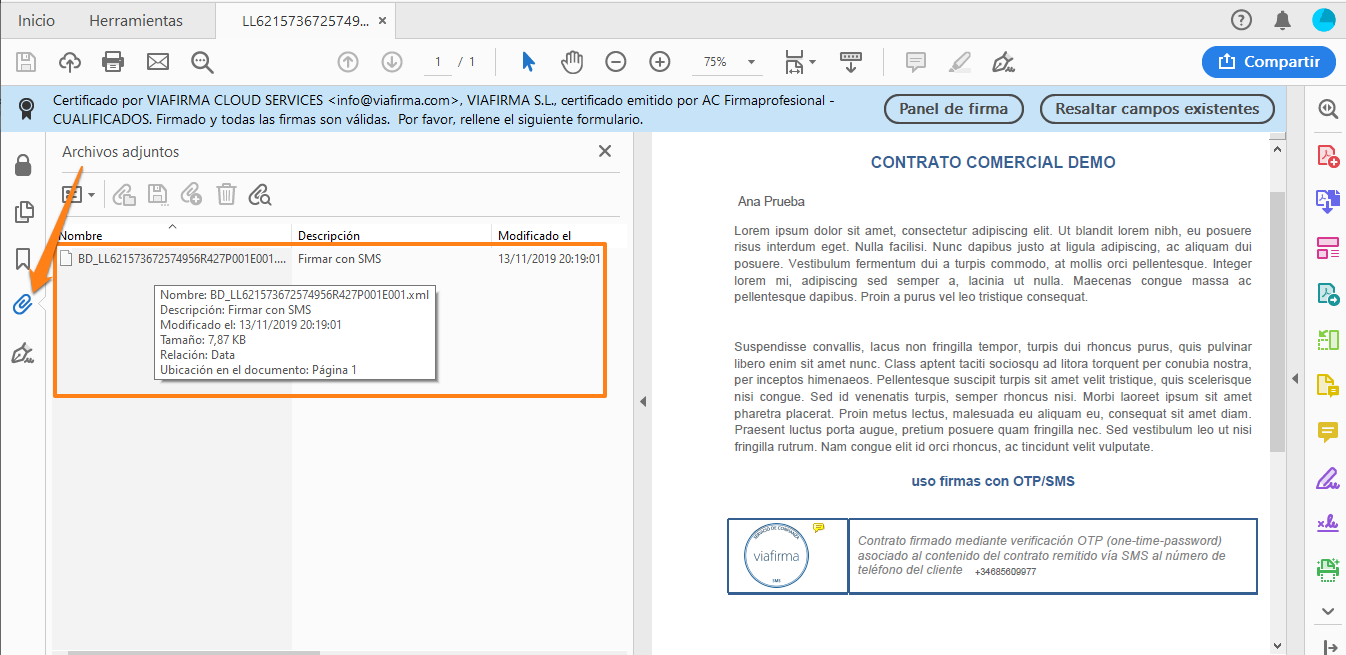
This is a file in XML format containing all the signature information with OTP-SMS (One Time Password).
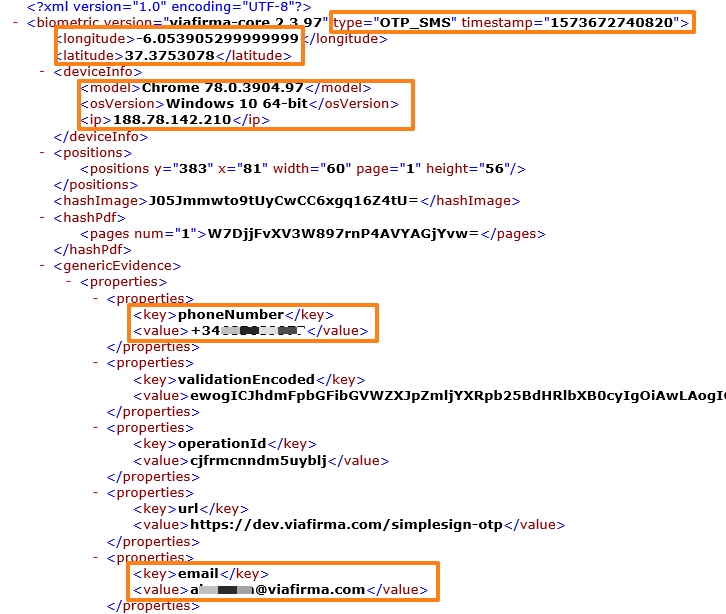
First we see timestamp information, this timestamp indicates the date and time when the evidence was collected, if we use a timestamp to “human time measurement” converter we will get something like the following:
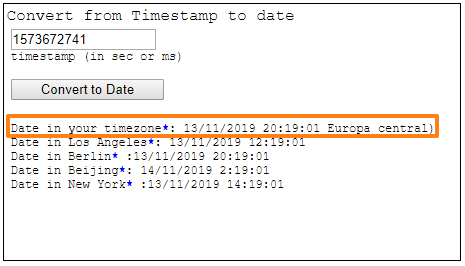
It was therefore collected on 13 November 2019 at 20 hours, 19 minutes and 01 second local time.
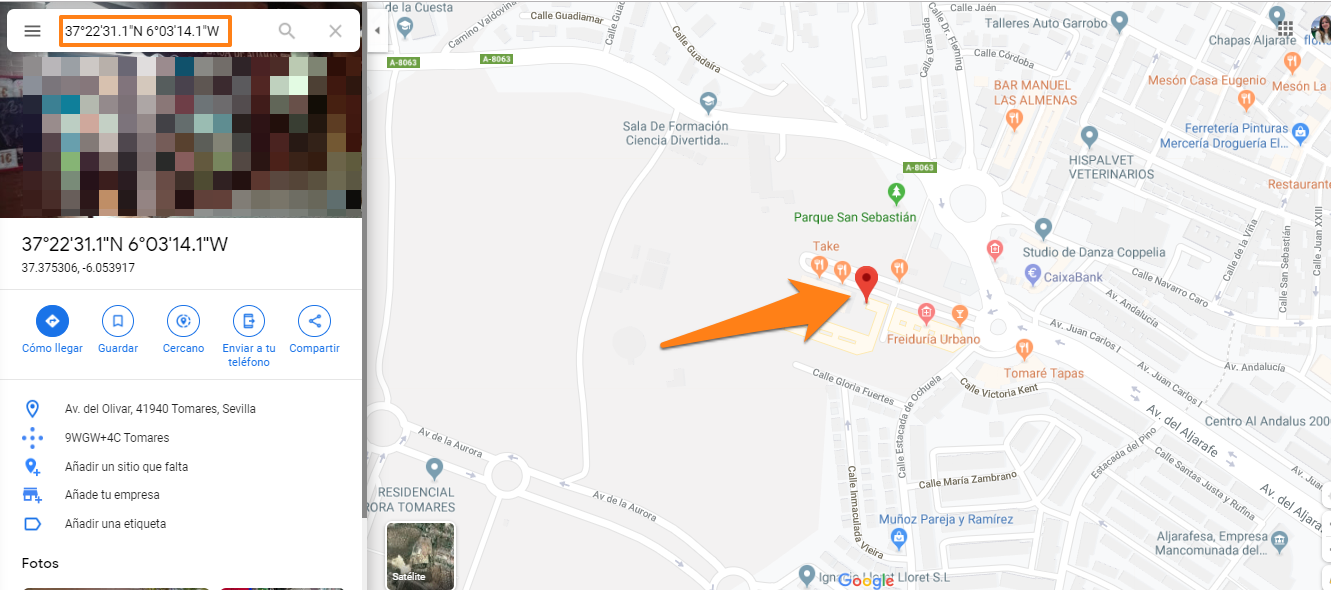
Below we have information on the approximate location of where the document has been electronically signed, by entering the latitude and longitude data in Google Maps, we will obtain the result:
In the next highlighted part of the document we have information on the device used by the signatory.
Then the telephone number to which the code was sent as well as the email address to which the request was sent.
As can be seen, more information is collected than if the document had been signed on paper.
Electronically signed document with biometric signature

In this case, depending on the device used to collect the signature, we can speak of a biometric signature itself.
If performed on one of these devices, biometric data such as speed, inclination, pressure …. will be collected.
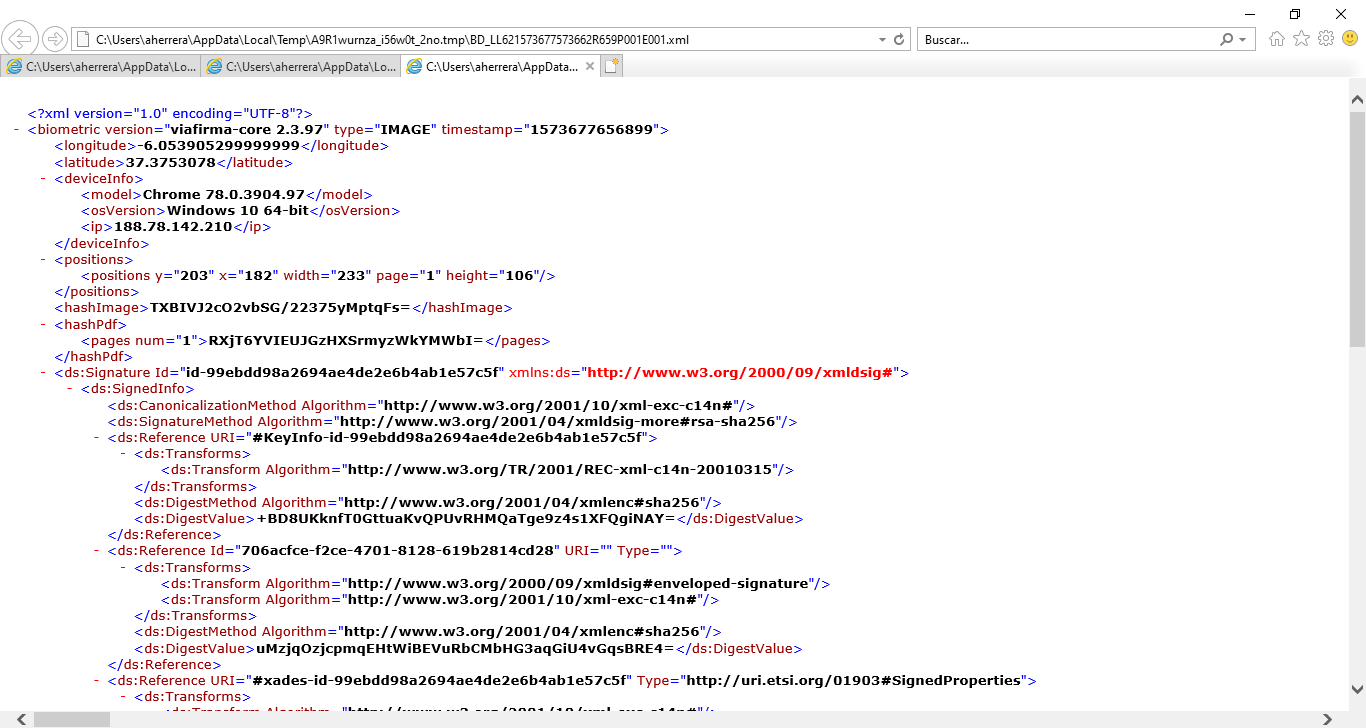
In case it is done from another device, such as a PC (with the mouse) or a mobile phone (with the finger) this data will not be collected. In the following image we can see an example of the attached XML file that would be generated.

As we can see, pressure values like “pressureMaxValue” and “pressureMinValue” are set to zero in this case.
If the signature had been captured on a device capable of collecting biometric data, the values would be encrypted to prevent anyone else from reproducing the same signature.
Other types of evidence in an electronically signed document
In addition to the digital certificate, OTP-SMS and biometric signature, our tool Viafirma Documents includes several options for the digital signature of documents, such as using the fingerprint, widely used in Latin American countries, as well as collecting other evidences that can be very useful depending on the use case.
Imagen
In many cases it can be very practical to add an image to the document (label, photograph after a repair, ….). It will also be effective when we need our signatory to provide his documentation, let’s see an example of the latter:

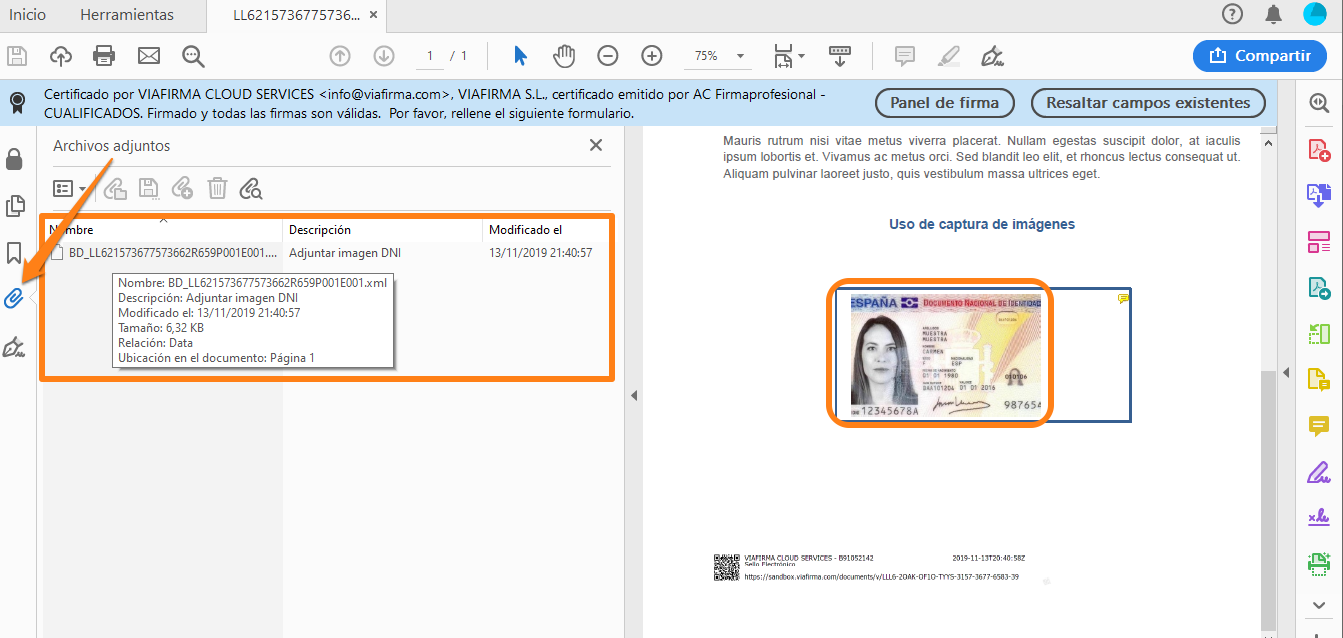
In addition to the DNI image itself, the incorporation of this type of evidence also generates an XML file attached to the PDF itself in which all the data relating to the attachment of the image can be viewed.
Advanced checks
One of the most useful evidences when signing a contract/document can be the advanced checks. They will be very practical to explicitly capture voluntary acceptances of the signatory highlighting critical or particularly important clauses or conditions, e.g. those clauses recommended by GDPR, MIFID II, etc.
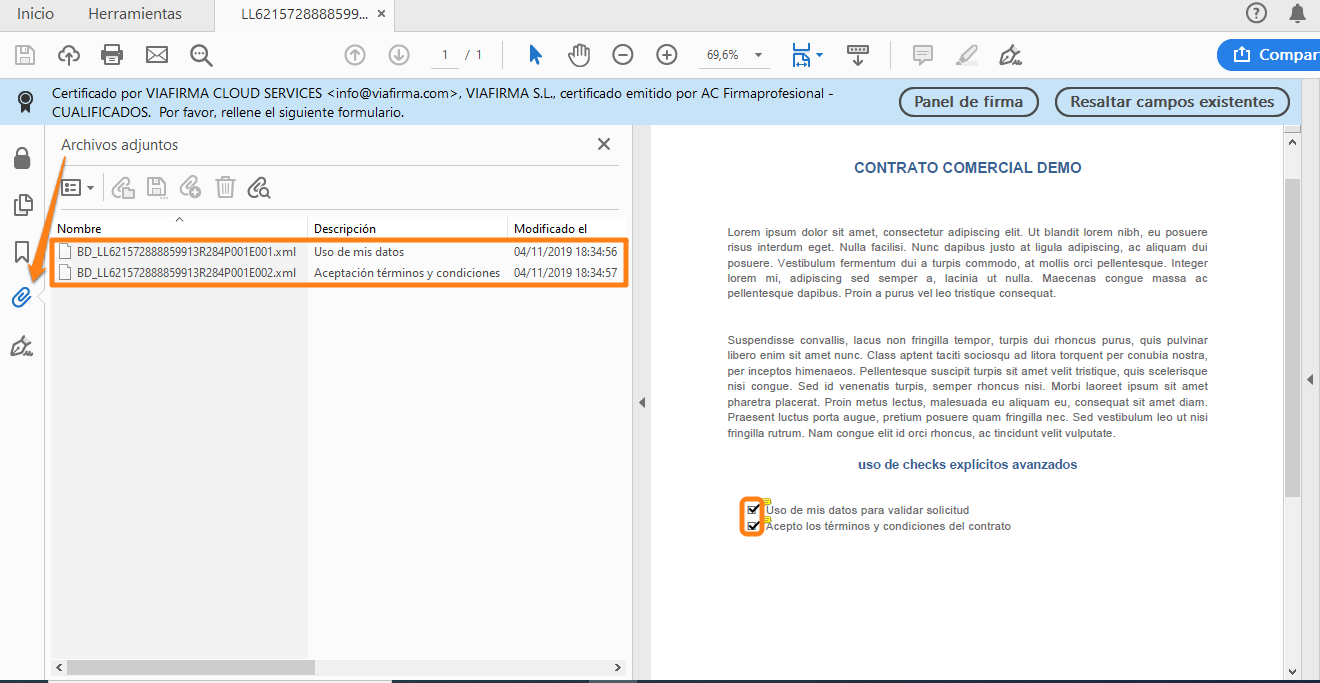
As in the rest of the evidences, in addition to the graphic representation of the check, an XML attachment containing all the information of that evidence will be generated in the PDF file itself.
In the example case we see that the signatory explicitly:
- You have given your consent to the use of your data for the processing of the application.
- You have accepted the terms and conditions of this contract.

All this information will always be available and accessible in the signed document itself.
However, as we know that it can be somewhat complicated to interpret, together with the signed document, what is commonly known as the “Audit-trail” or “Signature Audit” is generated. It brings together all the evidence and events collected during the signing process in a clear and orderly way, but fully understandable to the user.

Although the Audit Trail is of great help in providing clear, simple and quick access to all the information on the signature process, we must reiterate that it is the document itself that proves that it is electronically signed, as it contains all the information on the signatures and evidence captured during the process.
In addition to what we have seen above, Viafirma Documents offers a wide range of possibilities, such as fingerprint capture, voice or video.
